If you juggle multiple papers, paywalls, and looming deadlines, literature reviews eat time and sanity. Searching countless databases, vetting citations, and formatting references drains hours you could spend writing or experimenting.
I’ve used the tool in real workflows—and the promise is bold: Automated literature scanning (1,750 papers searched), 325 initially flagged, 72 more found via citations, and the top 20 synthesized into a structured report with APA links and hover previews.
Imagine instant language toggles (Chinese, English, Japanese), Browser Control that reaches paywalled content via institutional IP, and accurate, clickable references. Users praise fast support and honest citations—though occasional downtime happens.
In this SciSpace Review, I’ll cut through the hype and show which features matter for academics and industry researchers, how the Deep Review works step-by-step, and whether this platform truly speeds research. Let’s dive in.
Key Takeaways: SciSpace Review
- The Deep Review automates literature synthesis from thousands of papers into a top-20 report.
- Features include language switching, APA with hover links, and Browser Control for paywalled content.
- Real users report strong support and trustworthy references; occasional downtime is noted.
- Ideal for academics, grad students, and R&D professionals juggling multiple projects.
SciSpace Review: An Overview
Raamish’s Take
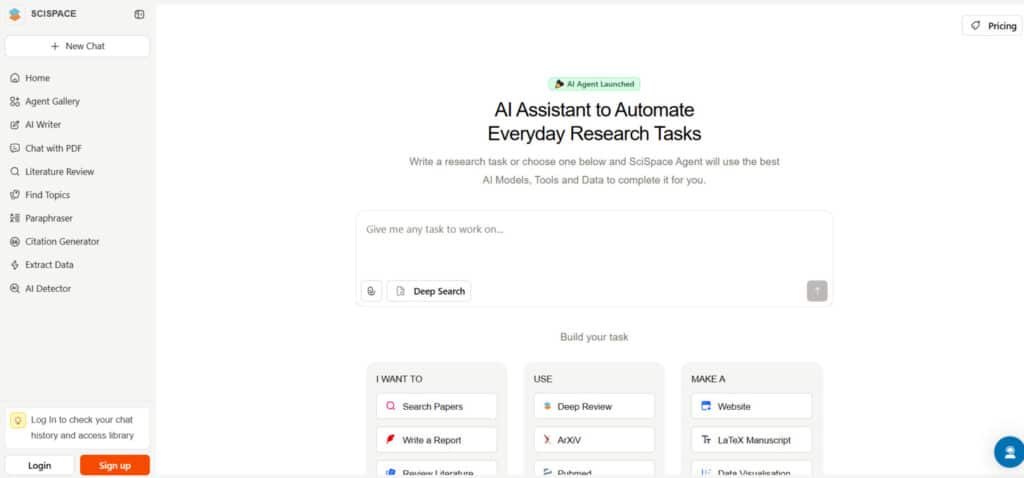
SciSpace streamlines research tasks with a smart AI assistant, tackling everything from paper searches to data analysis. It leverages top AI models and tools, letting you input tasks or pick from options like drafting manuscripts or creating charts.
The platform shines with standout features like deep review across ArXiv and PubMed, literature review support, and citation generation for seamless writing.
Data extraction and AI-powered notebooks boost efficiency, while custom outputs like LaTeX or PPTs cater to diverse needs, trusted by researchers globally.
Overwhelmed by research workloads? SciSpace automates the grind, delivering results fast.
Introduction to SciSpace
In the current AI landscape, an AI research assistant must do more than summarize—it must trace evidence, retrieve paywalled items, and deliver defensible results. I find this is the central point when you judge any modern academic tool.
Company background and purpose: The platform launched to compress weeks of reading into hours. It targets students, lab teams, and industry researchers who need repeatable workflows. The idea is simple: search, filter, expand via citations, rank, and synthesize into a clear literature review you can cite.
User feedback matters. Many users praise top-notch academic features, quick help, and genuine references. Free version users still get fast insights (limited downloads and AI summaries), while paid plans add full exports and access-aware retrieval.
There are trade-offs: some users report weekend downtime and occasional chat-with-PDF glitches, and cost is a common discussion. Still, for researchers who need speed, trust, and transparent evidence trails, this option often earns a spot on the shortlist.
- Why it fits: emphasis on speed, accuracy, and access-aware workflows.
- Who benefits: academics, educators, and R&D teams under deadline pressure.
What is SciSpace?
Imagine typing a research question and getting a traceable literature map in minutes. At its core, SciSpace is an AI research assistant that turns a single question into a structured literature review through a tight, repeatable process.
How it works under the hood
I start by answering clarifying prompts. The system uses those answers to set scope and metrics for the topic. Then the model runs a wide search across the literature.
In one example run, the search returned 1,750 hits, filtered to 325 relevant items, added 72 citation-linked papers, and ranked the set. The top 20 papers are synthesized into the final report.
The output shows APA-style references with clickable links and hover previews. You can toggle numeric formatting or switch to list view instantly. Language changes (English, Chinese, Japanese) apply without repeating the pipeline.
Who benefits most
Students, educators, and researchers get fast, defensible results. Students save time on theses. Educators pull reading lists or syllabi. Cross-disciplinary teams get traceable evidence when decisions matter.
The workflow reduces noisy claims by linking every claim back to the selected papers. That makes your work easier to defend and faster to iterate.
| Pipeline Stage | What Happens | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Query & Clarify | Initial question + prompts set scope | Refined search terms |
| Search & Filter | 1,750 hits → 325 relevant | Curated set of papers |
| Citation Expansion | Finds forward/backward links (+72) | Expanded, more robust set |
| Rank & Synthesize | Top 20 selected and summarized | Structured literature review with APA links |
Best Features of SciSpace
What matters most are the tools that reduce friction from discovery to draft—here’s what stood out.
SciSpace empowers users to navigate the vast world of research papers with ease, offering a suite of tools that simplify deep research, enhance writing, and deliver actionable insights.
Whether you’re drafting articles, conducting a deep review, or extracting information from complex documents, SciSpace’s features cater to diverse academic needs.
Below, we detail the platform’s capabilities, showcasing how it transforms the lot of work involved in scholarly tasks into a seamless, efficient process.
1. Literature Search and Discovery
SciSpace’s search function queries over 270 million research papers from sources like PubMed, arXiv, and Semantic Scholar, making deep research accessible and efficient.
- AI-Powered Semantic Search: Identifies relevant articles based on conceptual understanding, with filters for publication date, journal impact factor, open access status, and methodology. For example, a query on renewable energy yields precise results tailored to your focus.
- Literature Review Assistant: Generates summaries, highlights key findings, and maps citations to uncover research gaps and trends, saving a lot of time in synthesizing information.
- Deep Review: Automates end-to-end literature review by running a broad search (e.g., 1,750 hits), filtering to a focused set (e.g., 325), expanding via citations (e.g., +72), ranking results, and distilling the top 20 into a readable literature review, ideal for comprehensive deep research.
- Connected Papers Visualization: Displays graphical networks of related articles, authors, topics, and references, offering insights into research connections.
- Library Management: Saves and labels research papers for organized access, with tagging and folder systems for project-specific workflows.
- Export and Citation Management: Supports exports in BibTeX, RIS, and EndNote formats, integrating with Zotero and Mendeley for seamless writing workflows.
- Topic Exploration: Provides AI-curated topic pages with timelines, influential papers, and emerging trends, delivering insights for deep research.
2. PDF Interaction and Analysis (ChatPDF)
The ChatPDF feature enables conversational interaction with uploaded or web-based PDFs, transforming static documents into dynamic sources of information.
- Multi-Format Query Support: Handles natural language questions on content, methods, results, or figures, delivering quotes, paraphrases, and visualizations for quick insights.
- AI Copilot: Provides concise summaries for specific sections (e.g., methods, figures) and generates table-ready synopses for protocols or data, streamlining writing tasks.
- Multi-Document Chats: Compares up to 5 PDFs simultaneously (premium tiers) for comparative analyses and synthesized insights, perfect for cross-referencing articles.
- Supported File Types: Processes PDFs, DOCX, and scanned documents via OCR, with limits of 100 MB file size and 500 pages, accommodating a lot of document types.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Shares chat sessions via links with real-time editing and commenting, supporting collaborative writing and review.
- AI Enhancements: Offers contextual understanding of figures, tables, and appendices, with multilingual support for queries in over 20 languages.
- Language Switching: Flips outputs between languages (e.g., English↔Chinese) without re-running queries, ensuring no data loss for international teams.
3. AI Writing and Composition (AI Writer)
SciSpace’s AI Writer is a powerful feature for generating original academic content, addressing the lot of challenges in scholarly writing.
- Content Generation Modes: Produces abstracts, introductions, literature reviews, methods, and discussions from prompts or outlines, ideal for drafting articles.
- Customization Options: Adjusts tone, length, and style (APA, MLA), incorporating domain-specific terminology for precise writing.
- Input/Output Flexibility: Accepts text, outlines, or voice notes; outputs in DOCX, LaTeX, or Markdown, catering to varied writing needs.
- Plagiarism and Originality Checks: Scans against 270 million papers, ensuring <5% similarity to maintain authenticity in writing.
- Language Switching: Supports multilingual outputs (e.g., English↔Chinese) for drafts, preserving context and citations for global writing projects.
- Use Cases: Facilitates grant proposals, theses, and journal manuscripts with iterative refinement, simplifying complex writing tasks.
4. Paraphrasing and Editing (Paraphraser)
This feature refines text for clarity, conciseness, and academic integrity, enhancing the quality of writing.
- Rephrasing Modes: Offers standard, fluent, concise, or expansive modes, with tone adjustments for formality or technicality.
- Length and Structure Controls: Expands or contracts text by up to 50%, with sentence- or paragraph-level processing for flexible writing.
- Academic-Specific Features: Retains citations, equations, and terms; integrates with writing suites for seamless editing.
- Quality Assurance: Provides readability scores, grammar checks, and plagiarism scanning to ensure polished writing.
- Writing Aids: Paraphrases text within the library, integrating with saved papers for efficient writing workflows.
- Batch Processing: Handles up to 10,000 words, with export to Word or Google Docs for versatile writing applications.
5. Concept Explanation and Mapping (Concepts)
Breaks down complex scientific ideas into accessible formats, supporting deep research and learning.
- Concept Library: Maintains over 1 million pre-built explanations for terms, theories, and methodologies.
- Interactive Search: Queries by keyword or context for definitions, examples, and related concepts, providing information for researchers.
- Relationship Mapping: Generates graphs showing interconnections across disciplines, offering insights into concept networks.
- Educational Tools: Includes quiz generators, flashcards, and multilingual explanations for teaching and learning.
- Research Applications: Aids hypothesis formulation by highlighting concept gaps, enhancing deep research.
6. Citation and Reference Management (Citation Generator)
This function ensures precise citations across over 9,000 styles, streamlining writing and submission processes.
- Input Methods: Auto-populates via DOI, PMID, URL, ISBN, or manual entry; supports bulk import from RIS/BibTeX.
- Output Formats: Generates in-text citations, footnotes, and bibliographies in RTF, HTML, or LaTeX.
- Citations & References: Uses APA by default with clickable links and hover previews; switches to numeric styles (e.g., Vancouver); tracks references to reduce manual cleanup for submissions.
- Style Coverage: Covers APA, MLA, Chicago, IEEE, and custom styles; handles diverse sources for comprehensive writing.
- Advanced Tools: Validates cross-references, detects duplicates, and sorts citations for accuracy.
- Integration: Embeds via browser extension or API, enhancing writing workflows.
7. Data Extraction and Tabulation (Extract Data)
Automates retrieval of structured information from documents, optimizing deep research tasks.
- Extraction Categories: Extracts tables, figures, chemical structures, and metadata for analysis.
- Supported Inputs: Processes PDFs, images, and HTML; supports batch processing for up to 50 documents.
- AI Accuracy: Achieves 95% precision using computer vision and NLP; offers customizable templates for data extraction.
- Output Options: Exports to CSV, Excel, or JSON; generates visualizations from extracted data.
- Use Cases: Supports meta-analyses, evidence synthesis, and dataset curation for research.
8. AI Content Detection (AI Detector)
Identifies machine-generated text to ensure authenticity in writing.
- Detection Algorithms: Analyzes perplexity, burstiness, and stylistic markers; supports English, Spanish, and French.
- Accuracy Metrics: Achieves 98% detection rate for AI-generated text; <2% false positives.
- Reporting: Provides scores (0-100% AI likelihood), highlighted segments, and rewrite suggestions for writing integrity.
- Writing Aids: Runs AI-detection checks on paraphrased or generated text to ensure originality.
- Integration: Embeds in writing tools; scans up to 50,000 words in batches.
9. Access and Authentication
Facilitates seamless access to scholarly content, addressing access needs.
- Browser Control & Access Rights: Uses institutional IP or proxy services (e.g., EZproxy) to fetch paywalled papers, bridging the gap between discovery and full-text access.
- Integration: Browser extension enables one-click access to papers via institutional credentials, subject to subscription availability.
10. Presentation and Export Tools
Enhances dissemination of research outputs for various audiences.
- Export Helpers: Converts literature reviews or extracted data into slide outlines (PowerPoint) or short video summaries (MP4) for presentations.
- Use Cases: Ideal for conference talks, classroom teaching, or stakeholder briefings.
- Integration: Works with saved papers and AI-generated content from the library or ChatPDF.
11. Additional Platform-Wide Functionalities
- Manuscript Formatting: Offers over 100,000 journal templates for publisher compliance, aiding writing and submission.
- Collaboration Suite: Enables real-time co-editing, version control, and feedback loops for collaborative writing.
- Plagiarism Checker: Scans against 99 billion web pages and 270 million papers to ensure originality.
- Browser Extension: Provides one-click PDF uploads, highlighting, and annotations for efficient deep research.
- Mobile App: Offers iOS/Android access for searches and chats on the go.
- API and Integrations: Connects with Overleaf, Google Scholar, and ORCID for streamlined workflows.
- Analytics Dashboard: Tracks reading time, citation impact, and productivity, providing insights for researchers.
“The net effect: less format wrangling, more analysis.”
| Feature | What it does | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Review | Automated retrieval → filter → expand → rank → synthesize | Saves hours; produces a traceable top-20 literature review |
| Chat with PDFs | Q&A and plain-language summaries of sections | Makes dense text usable for fast decisions |
| Browser Control | Access-aware retrieval using institutional IP | Gets you the full text behind paywalls |
| Library & Exports | Organize sources; export slides/videos | Speeds writing and presentations |
- Search filters & ranking: Start broad, narrow by year/venue, and surface the most relevant papers fast.
- Net result: These features reduce friction from discovery to write-up so you can focus on analysis.
Pricing Plans of SciSpace
Cost matters when you move from casual scoping to full write-ups. Below I break down what each option gives you and when upgrading makes sense.
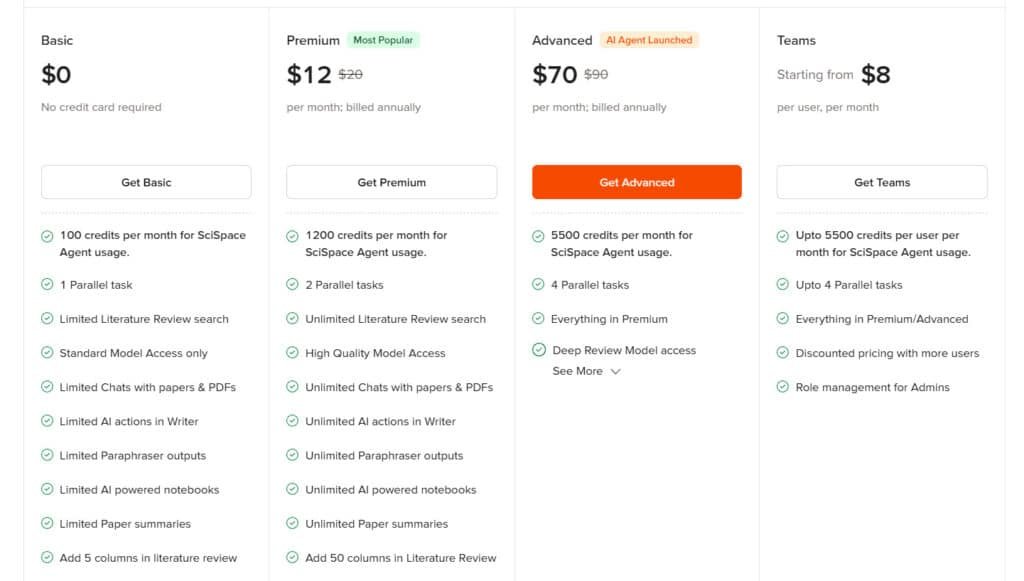
SciSpace offers tiered plans with monthly and annual billing. Basic is free, while higher tiers unlock unlimited AI tools. Annual plans save 40%.
Basic Plan
Free, no credit card needed. Includes 100 credits/month, 1 parallel task, limited literature review, standard model, limited chats, AI actions, paraphraser, notebooks, summaries, 5-column literature review, limited citations, topics, podcasts, AI detections, no exports.
Premium Plan
Monthly: $20 (sale: $14); Annual: $12/month ($144/year, sale: $8.40/month). Offers 1200 credits/month, 2 parallel tasks, unlimited literature review, high-quality model, unlimited chats, AI actions, paraphraser, notebooks, summaries, 50-column literature review, citations, topics, podcasts, AI detections, exports (RIS/CSV/BIB/Excel/XML), customizable chat settings.
Advanced Plan
Monthly: $90 (sale: $63); Annual: $70/month ($840/year, sale: $49/month). Includes Premium features, 5500 credits/month, 4 parallel tasks, Deep Review model access.
Teams Plan
Monthly: $18/user; Annual: $8/user/month. Up to 5500 credits/user/month, 4 parallel tasks, Premium/Advanced features, discounted pricing, role management.
| Plan | Monthly Price | Annual Price (per month) | Credits/Month | Parallel Tasks | Unlimited Literature Review | Deep Review Access |
| Basic | $0 | $0 | 100 | 1 | Limited | No |
| Premium | $20 ($14 sale) | $12 ($8.40 sale) | 1200 | 2 | Yes | No |
| Advanced | $90 ($63 sale) | $70 ($49 sale) | 5500 | 4 | Yes | Yes |
| Teams | $18/user | $8/user | Up to 5500 | Up to 4 | Yes | Yes |
“Support is responsive on subscription issues and refunds—useful if you need to switch plans.”
When to upgrade: move to a paid subscription when exporting, citation formatting, or managing many references eats time.
For lab teams or faculty, paid plans can centralize work and cut duplicated effort—so the subscription often pays back quickly.
Pros & Cons of SciSpace
If you need quick, defensible results, this platform often delivers—fast and with verifiable sources. Below I list what I liked and what to watch for when you plan projects around it.
Pros
- Speed to results: The Deep Review gets you from prompt to a usable summary fast, saving serious time on initial scoping.
- Genuine references: Outputs include verifiable citations and APA links, so you can trust the sources for coursework or a thesis.
- Deeper synthesis: For complex topics the summaries go beyond keywords—helping you understand trends without skimming dozens of papers.
- Multi-language support: Instant language switching works well for bilingual teams and international literature checks.
- Strong support: Users report timely help—plan changes, refunds, and troubleshooting tend to be handled quickly.
Cons
- Occasional downtime: Some users note weekend chat-with-PDF hiccups; don’t schedule final deadlines at the last minute.
- Paper cap per run: The top-20 limit means exhaustive surveys need multiple passes or extra tooling to reach full breadth of literature.
- Subscription cost: If you only need occasional checks, the subscription can feel pricey—time your upgrades around big deliverables.
Summary: It excels at speed, multilingual clarity, and trustworthy references. If you need exhaustive breadth in one pass, plan additional runs or try alternatives next.
“The net effect: less format wrangling, more analysis.”
Alternatives to SciSpace
Not every tool is built to do everything—some excel at mapping, others at extraction. If you need more than synthesis, combining tools gives better coverage. Below I list options and how they fit into a typical workflow.
SciSpace excels at chatting with PDFs, extracting tables, and searching 280M+ papers for lit reviews—making research feel effortless at $20/month Premium. These eight tools complement or expand on its strengths with drafting, editing, or deeper citation help.
Paperpal
Paperpal offers real-time grammar, plagiarism checks, and journal templates across 250M+ papers. Ideal for submission-ready polish—$25/month – Read Full Review
JenniAI
JenniAI co-writes theses with autocomplete, outlines, and citation handling. Great for long drafts—free tier, $20/month unlimited – Read Full Review
JotbotAI
Jotbot AI turns voice/video notes into cited drafts that match your style. Students juggling lectures save time—free basics, $14/month – Read Full Review
ScholarAI
ScholarAI searches 200M+ papers, builds citation graphs, and answers with sources. Integrates with Zotero—free tier, $9.99/month Pro – Read Full Review
PDF AI
PDF AI chats with documents, extracts tables, and pulls exact quotes with page numbers. Quick insights—free for small files, $17/month Pro – Read Full Review
SpeakAI
Speak AI transcribes lectures/videos and generates summaries or flashcards. Multilingual support shines—$29/month Pro – Read Full Review
WordVice
WordVice refines tone, paraphrases, and checks clarity for non-natives. Seamless Overleaf sync—$19/month Premium – Read Full Review
AI-Writer
AI-Writer (Writefull) generates abstracts, paraphrases, and academic phrases tuned for scholarly work—€10.58/month yearly – Read Full Review
These shift from SciSpace’s PDF focus to drafting or citation depth—choose based on your workflow stage.
| Tool | Key Strengths | Starting Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| SciSpace | PDF chat, table extraction, 280M+ papers | $20/month | Literature reviews |
| Paperpal | Grammar/plagiarism, journal templates | $25/month | Submission polish |
| JenniAI | Co-writing, outlines, citations | $20/month | Theses & long drafts |
| Jotbot AI | Voice notes, style match, instant cites | $14/month | Lecture-based essays |
| ScholarAI | Citation graphs, 200M+ papers | $9.99/month | Deep research & gaps |
| PDF AI | Document chat, exact quotes | $17/month | Quick PDF insights |
| Speak AI | Transcription, multilingual summaries | $29/month | Lectures & audio notes |
| WordVice | Paraphrasing, non-native clarity | $19/month | Tone refinement |
| AI-Writer | Abstracts, scholarly phrasing | €10.58/month | Quick rewrites |
“No single app wins every scenario; the best stack balances discovery breadth, ranking quality, and synthesis speed.”
My rule of thumb: Use mapping tools to find topics, extraction tools to triage, and hand the baton to the synthesis platform for final literature synthesis. That mix keeps your workflow fast and defensible.
Case Study / Personal Experience with SciSpace
I ran a live case to see how a broad question turns into a focused literature review, and the results surprised me.
Real-World Results: From broad question to focused review with top 20 sources
I started with a broad question: Investigate if AI-based personalized feedback and assessment tools enhance student motivation in higher education. The system asked clarifying metrics (discipline, outcome measures) and then launched the search pipeline.
The run returned 1,750 hits, filtered to 325 relevant papers, added 72 via citation expansion, and synthesized the top 20 into a neat literature review. APA-style citations were clickable and showed hover previews—so I could verify sources fast.
My Experience: Refining questions, switching languages, and iterating for coverage
I switched language outputs for a collaborator (Chinese ↔ English ↔ Japanese) with zero re-run time. Where I wanted more breadth, I split the topic into sub-questions—pre-class prep, homework engagement, and in-class prompts—and ran separate steps.
- Hands-on step: refine the question, answer prompts, then run the pipeline.
- Key result: a ready-to-edit scaffold with 20 vetted sources and working citations.
- Time saved: hours reclaimed from formatting and reference wrangling.
“The iterative approach (refine, run, split) gave a richer set of literature than a single pass.”
What Users Care About Now
Readers want clear answers about accuracy, speed, and how that 20‑paper cap affects their final draft. I’ll walk through what matters and what I found in real runs.
Accuracy and trustworthiness of sources and citations
Accuracy: In my tests and reports from other users, references were genuine and recent. Clickable links and hover previews make it fast to verify any claim.
Transparency: The documented process—search → filter → citation expansion → ranking → synthesis—helps you trace why a paper made the cut.
Speed, reliability, and the impact of “only 20 papers” per review
Speed: The model delivers a usable literature review quickly, saving you real time. Plan extra buffer for weekends—some folks note occasional downtime.
20‑paper ceiling: This limits exhaustive surveys. I mitigate it by running focused follow-ups and merging outputs to surface more relevant papers without losing coherence.
Customer support and service: What recent users say
Support: Most users praise fast plan fixes and refunds. A slow chat happened to one user, but the team often asks for PDFs to diagnose issues—so that check is intentional.
“If you value trustworthy references, transparent steps, and responsive support, this tool checks the boxes—just plan around the 20‑paper limit.”
| Concern | What I saw | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy & citations | Genuine references; hover previews | Verify links; cite originals |
| Speed & reliability | Fast output; occasional weekend dips | Schedule runs before deadlines |
| Coverage (20 papers) | Top‑20 synthesis only | Run multiple focused passes |
Who Should Choose SciSpace?
Deciding which research assistant fits your workflow starts with the work you do and the way you need results delivered. I’ve used this kind of tool in thesis work and lab briefs, so here’s a practical guide to who benefits most—and when another tool might be smarter.
Best-fit users and use cases
Choose this platform if you’re an academic or practitioner who needs fast, defensible reviews. It shines on thesis chapters, grant background sections, and internal research briefs where clear citations matter.
- Students: Save hours on literature synthesis and citation formatting for theses and capstone projects.
- Educators: Update course readings quickly—especially in fast-moving topics—without wrestling with references.
- R&D teams: Run adjacent-topic passes, then merge outputs to overcome the 20-paper cap and produce coherent briefs.
- Multilingual labs: Instant language switching speeds collaboration across regions and contexts.
When another tool may be better
If your priority is mapping topic networks (visual discovery) or heavy PDF annotation and table extraction, pair this tool with a specialist.
- Use a mapping-focused app when you need network graphs or cluster exploration before synthesis.
- Pick a PDF-centric tool for deep annotation, data tables, or bulk extraction; let each tool do its best work.
- For occasional quick scans of a few papers, the free tier will often suffice; upgrade for polished exports and higher throughput.
“Bottom line: pick this tool when you value speed plus rigor; pick alternatives when your workflow centers on network mapping or heavy manual PDF work.”
How to Get the Most Out of SciSpace
Kick off with a wide question and refine it quickly; that small change improves search precision dramatically. Answer the platform’s clarifying prompts about metrics and scope so the pipeline knows what to prioritize.
- Break big questions into focused steps. Run parallel mini-reviews on subtopics (e.g., pre-class prep, homework). This expands literature coverage beyond the top-20 paper limit.
- Filter and scan ranked results. Prioritize recent literature, mark missing angles, and re-run targeted searches when needed.
- Use language switching smartly. Flip outputs to match collaborators—no extra runs required—then gather feedback and flip back.
- Leverage Browser Control and institutional access. Log in via your university so the browser can pull paywalled full-text PDFs automatically.
- Organize as you go. Save tagged papers in the library, pull key text snippets with the AI copilot, and generate citations early to avoid formatting crunches.
- Final assembly tip. Merge runs and create a short table summarizing study design, metrics, and main findings to sharpen your narrative before peer review.
| Quick Check | Action | Why it helps |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Enable institutional login | Full-text retrieval for paywalled papers |
| Search | Use filters (year, venue) | Surfaces the most relevant papers |
| Work | Tag library items | Build a reusable evidence set |
Conclusion: SciSpace Review
Raamish’s Take
SciSpace streamlines research tasks with a smart AI assistant, tackling everything from paper searches to data analysis. It leverages top AI models and tools, letting you input tasks or pick from options like drafting manuscripts or creating charts.
The platform shines with standout features like deep review across ArXiv and PubMed, literature review support, and citation generation for seamless writing.
Data extraction and AI-powered notebooks boost efficiency, while custom outputs like LaTeX or PPTs cater to diverse needs, trusted by researchers globally.
Overwhelmed by research workloads? SciSpace automates the grind, delivering results fast.
When deadlines loom, the real value is how quickly the tool turns scattered papers into a usable literature review you can share and edit.
I found the process transparent: The Deep Review, AI copilot, citations, language switching, and Browser Control connect questions to paper-ready content. Users get genuine citations, fast results, and helpful support—though occasional downtime and the 20‑paper cap mean you should plan iterative runs.
My recommendation: Start with the free tier to test fit. If it speeds your research, upgrade to the full version. Refine prompts, split big questions, and keep references organized as you go.
Final point: If traceable citations, speed, and multilingual output matter, give it a scoped run today—your next article draft will thank you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does this AI research assistant do?
It automates literature discovery and synthesis — from retrieving relevant papers to ranking, summarizing, and generating formatted citations. I find it especially helpful for turning a broad question into a focused review with a shortlist of top sources.
Can it access paywalled articles through my institution?
Yes — with browser control and institutional IP access enabled, it can reach paywalled full text just like you would through your university network. You’ll need to grant the tool the appropriate browser permissions or use institutional login methods.
How accurate are the citations and references it creates?
It produces APA and numeric formats and provides clickable links for traceability. I still double-check automatically generated references for missing page ranges or author order — it’s solid but not perfect every time.
How many papers can a single literature review include?
Reviews typically synthesize a limited set — often the top 20 sources by relevance. That makes the output focused, but if you need exhaustive coverage you’ll want to iterate or supplement with manual searches.
Does it support non-English output and multilingual searches?
Yes — you can switch output language without rerunning the entire pipeline. I’ve used it to generate plain-language summaries in Spanish and French with consistent results.
What writing aids are built in (paraphrasing, AI-detection, etc.)?
It includes paraphrasing tools, an AI-detector for checking originality, and a citation generator. These help maintain academic integrity, but I recommend combining them with your own editing and plagiarism checks.
Can I chat with and query PDFs directly?
You can. The AI copilot lets you ask specific questions about PDF content, extract plain-language explanations, and summarize complex sections on demand — useful during rapid reading sessions.
How does the tool rank search results and filter relevance?
It uses retrieval and relevance-ranking algorithms to cast a wide net and then prioritize papers by topical match, citation metrics, and recency. You can further refine with filters to focus the set.
What are the main plan differences — free vs paid?
Free tiers usually let you run basic queries and chat with limited daily usage. Paid plans increase review size, faster processing, export options (slides, short videos), and advanced features like browser control and institutional access. Annual subscriptions often lower the per-month cost.
Are there discounts or academic pricing available?
Yes — there are student and institutional discounts, plus occasional promo codes. Compare monthly vs annual billing to see where you save most based on your usage pattern.
What are common limitations I should expect?
Expect occasional downtime, caps on paper count per review, and costs that add up for heavy users. For exhaustive mapping or very large-scale systematic reviews, consider pairing with other academic discovery tools.
Which tools are good alternatives for mapping and discovery?
For broader discovery and visualization, I use Semantic Scholar, Connected Papers, and ResearchRabbit. For extraction and reading workflows, Scholarcy and Zotero plugins are solid complements.
How do I get the best results from the assistant?
Refine prompts, break big questions into focused subquestions, iterate, and leverage browser control for full-text retrieval. Save and organize sources in the research library so you can track coverage and gaps efficiently.
Is customer support responsive when issues arise?
Support has improved — many users report timely responses and helpful guidance. For urgent institutional access or billing problems, expect standard business-hour response times and escalation paths for paid plans.